Navigation auf uzh.ch
Navigation auf uzh.ch
Since the original description of quantal transmission, a defining feature of all synapses, it has become clear that trans-synaptic molecular signaling between the pre- and the post-synapse is key to proper brain function.
Trans-synaptic signaling is enabled by synaptic cell surface receptors and adhesion molecules, and is important for axon outgrowth, target-cell recognition, synapse formation, and maintaining transmission in mature synapses. Unraveling these mechanisms at a genetic and molecular level is of key importance.
Ultimately, this knowledge will lead to an understanding of how genetic mutations in these synaptic molecules lead to neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders in humans. It will also lead to a better understanding of how target-specific rewiring—the ability of which is lost during development—can be restored in mature neurons. Solving these problems is a prerequisite for brain repair after injury and could aid development of novel therapies for neurological disorders.
Recent publications:
Luo W, Cruz-Ochoa NA, Seng C, Egger M, Lukacsovich D, Lukacsovich T, Földy C (2022) Pcdh11x controls target specification of mossy fiber sprouting. Frontiers in Neuroscience 16:888362. Link
Seng C, Luo W, Földy C (2022) Circuit formation in the adult brain. European Journal of Neuroscience, 56(3):4187-4213. (Review) Link
Luo W, Egger M, Domonkos A, Que L, Lukacsovich D, Cruz-Ochoa NA, Szőcs S, Seng C, Arszovszki A, Sipos E, Amrein I, Winterer J, Lukacsovich T, Szabadics J, Wolfer DP, Varga C, Földy C. (2021) Recurrent rewiring of the adult hippocampal mossy fiber system by a single transcriptional regulator, Id2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 118(40):e2108239118. Link
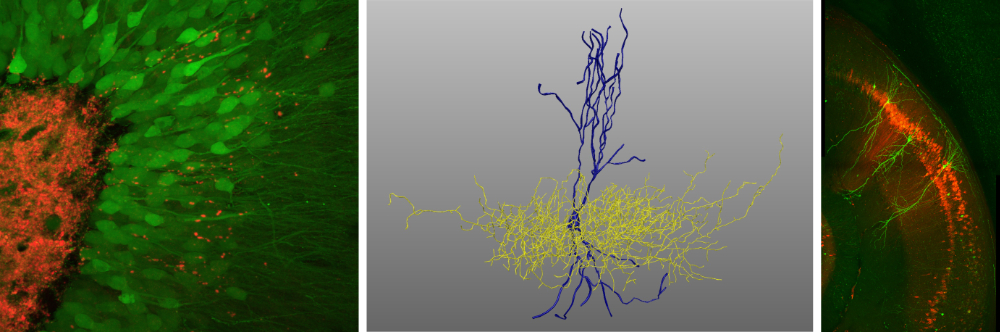
Neuronal diversity is a key property of the brain. This diversity helps to create different brain activity patterns and behavior. Cell type classification schemes have provided us with a detailed understanding of the distinct types that constitute this diversity and their contribution to brain function.
In recent years, the use of single-cell RNAseq significantly extended this existing framework, especially expanding our understanding of the molecular features of different neuronal types. Our work focuses on the transcriptomic survey of cortical, hippocampal and midbrain neurons.
Recent publications:
Beerens S, Winterer J, Lukacsovich D, Földy C*, Wozny C* (2022) Transcriptomically-guided pharmacological experiments in neocortical and hippocampal NPY-positive GABAergic interneurons. eNeuro. 9(2):ENEURO.0005-22.2022. (*Corresponding author) Link
Boxer EE, Seng C, Lukacsovich D, Kim J, Schwartz S, Kennedy MJ, Földy C, Aoto J (2021) Neurexin-3 defines synapse- and sex-dependent diversity of GABAergic inhibition in ventral subiculum. Cell Reports, 37(10):110098. Link
Que L*, Lukacsovich D*, Luo, W, Földy C (2021) Transcriptional and morphological profiling of parvalbumin interneuron subpopulations in the mouse hippocampus. Nature Communications, 12(1):108. (*Equal contributions) Link
Sticco MJ, Peña Palomino PA, Lukacsovich D, Thompson BL, Földy C, Ressl S, Martinelli DC (2021) C1QL3 promotes cell-cell adhesion by mediating complex formation FASEB J, 35(1):e21194. Link
Collins B, Pierre-Ferrer S, Muheim C, Lukacsovich D, Cai Y, Spinnler A, Gutierrez Herrera C, Wen S, Winterer J, Belle MDC, Piggins HD, Hastings M, Loudon A, Yan J, Földy C, Adamantidis A, Brown SA (2020) Circadian VIPergic neurons of the suprachiasmatic nuclei sculpt the sleep-wake cycle. Neuron, 108(3):486-499. Link
Oláh VJ, Lukacsovich D, Winterer J, Arszovszki A, Lőrincz A, Nusser Z, Földy C, Szabadics J (2020) Functional specification of CCK+ interneurons by alternative isoforms of Kv4.3 auxiliary subunits. Elife, 9:e58515. Link
Steinberg EE, Gore F, Heifets BD, Taylor MD, Norville ZC, Beier KT, Földy C, Lerner TN, Luo L, Deisseroth K, Malenka RC (2020) Amygdala-midbrain connections modulate appetitive and aversive learning. Neuron, 106(6):1026-1043.e9. Link
Cerniauskas I, Winterer J, de Jong JW, Lukacsovich D, Yang H, Khan F, Peck JR, Obayashi SK, Lilascharoen V, Lim BK, Földy C*, Lammel S* (2019) Chronic stress induces activity, synaptic and transcriptional remodeling of the lateral habenula associated with deficits in motivated behaviors. Neuron, 104(5):899-915.e8. (*Corresponding author) Link
Winterer J*, Lukacsovich D*, Que L, Sartori AM, Luo W, Földy C (2019) Single-cell RNAseq characterization of anatomically-identified OLM interneurons in different transgenic mouse lines. European Journal of Neuroscience, 50(11):3750-3771. (*Equal contributions) Link
Lukacsovich D*, Winterer J*, Que L, Luo W, Lukacsovich T, Földy C (2019) Single-cell RNAseq reveals developmental origins and ontogenetic stability of neurexin alternative splicing profiles, Cell Reports, 27(13):3752–3759. (*Equal contributions) Link
Que L, Winterer J, Földy C (2019) Deep survey of GABAergic interneurons: Emerging insights from gene-isoform transcriptomics. Front Mol Neurosci, 12:115. Link